Ever wondered how your brain works? Neuphony can help you understand it!
Your brain is like a busy orchestra, with different parts working together. We’ll explore what brain waves are (Theta, Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta) and how they affect your thinking, feeling, and sleep.
Discover how scientists are learning more about the brain and how you can use this to improve your memory, focus, and overall mental health.
Ready to feel sharper and more in control? Let’s get started.
Decoding How Your Brain Works
Here, we’ll break down the amazing world of brain waves. These are like tiny traffic signals in your head, controlling your thoughts, feelings, and actions. We’ll explore different brain waves – Theta, Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta – and what they do. Plus, we’ll look at cool research that’s helping us understand them better.
The Brain’s Rhythmic Symphony
Certainly! Here’s the line with transition words added:
Imagine your brain as a bustling metropolis, where billions of neurons are constantly communicating with each other through electrical signals, forming intricate networks of thoughts and actions.
monitor brain waves drive mental activity, impacting mood and cognitive abilities. Understanding the different types of brain waves and how they interact provides valuable insights into the inner workings of the human mind.
Understanding Brain Waves
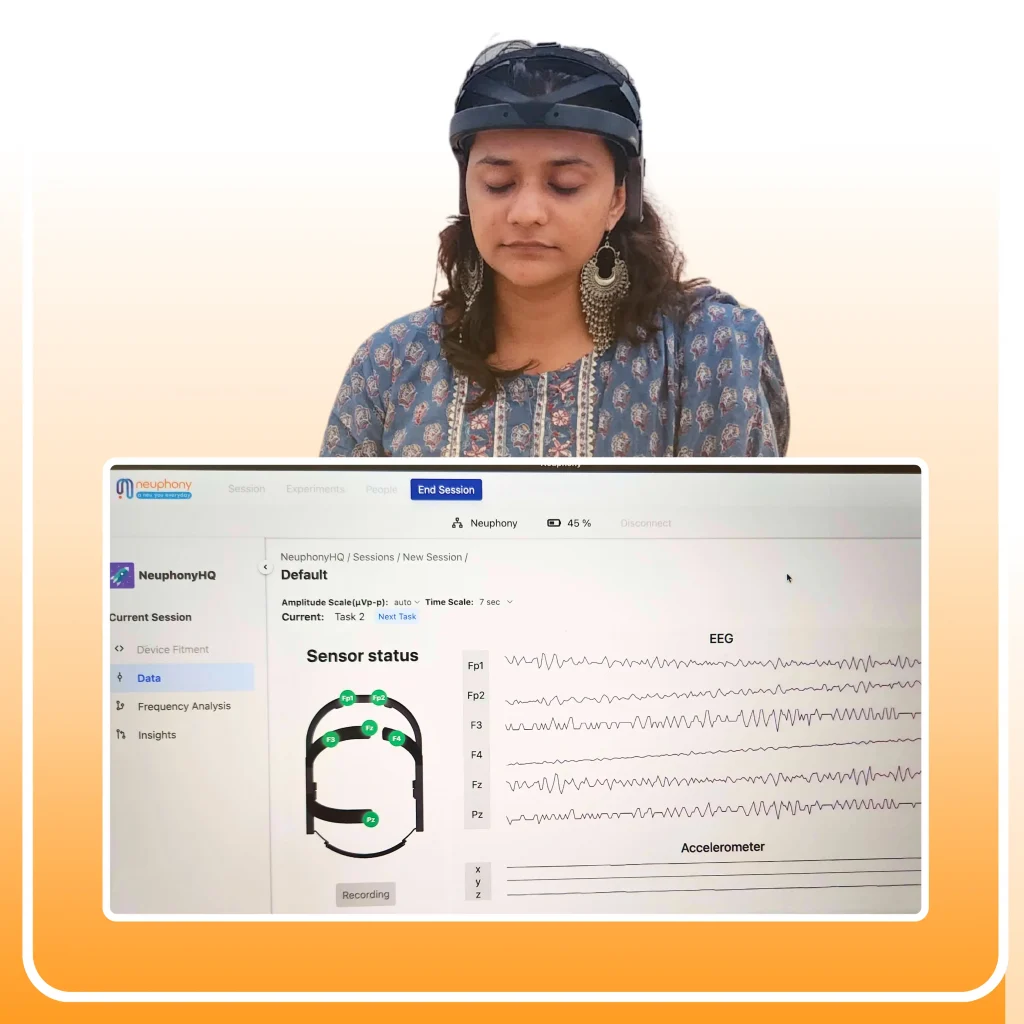
Brain waves, also known as neural oscillations, are rhythmic patterns of electrical activity generated by the synchronised firing of neurons in the brain. These oscillations can be measured using electroencephalography (EEG), a non-invasive technique that detects electrical signals on the scalp. Each type of brain wave is characterized by its frequency, amplitude, and location in the brain and serves a unique function in regulating cognitive processes.
Exploring the Power of Neurofeedback-based Meditation
Neurofeedback-based meditation is a technique that harnesses the power of sound or focused attention to modulate brain wave activity. By listening to specific frequencies or engaging in mindfulness practices, individuals can alter their brain waves to achieve desired states of consciousness, such as relaxation, focus, or deep sleep. Research has shown that regular meditation can lead to long-term changes in brain wave patterns, promoting overall well-being and mental resilience.
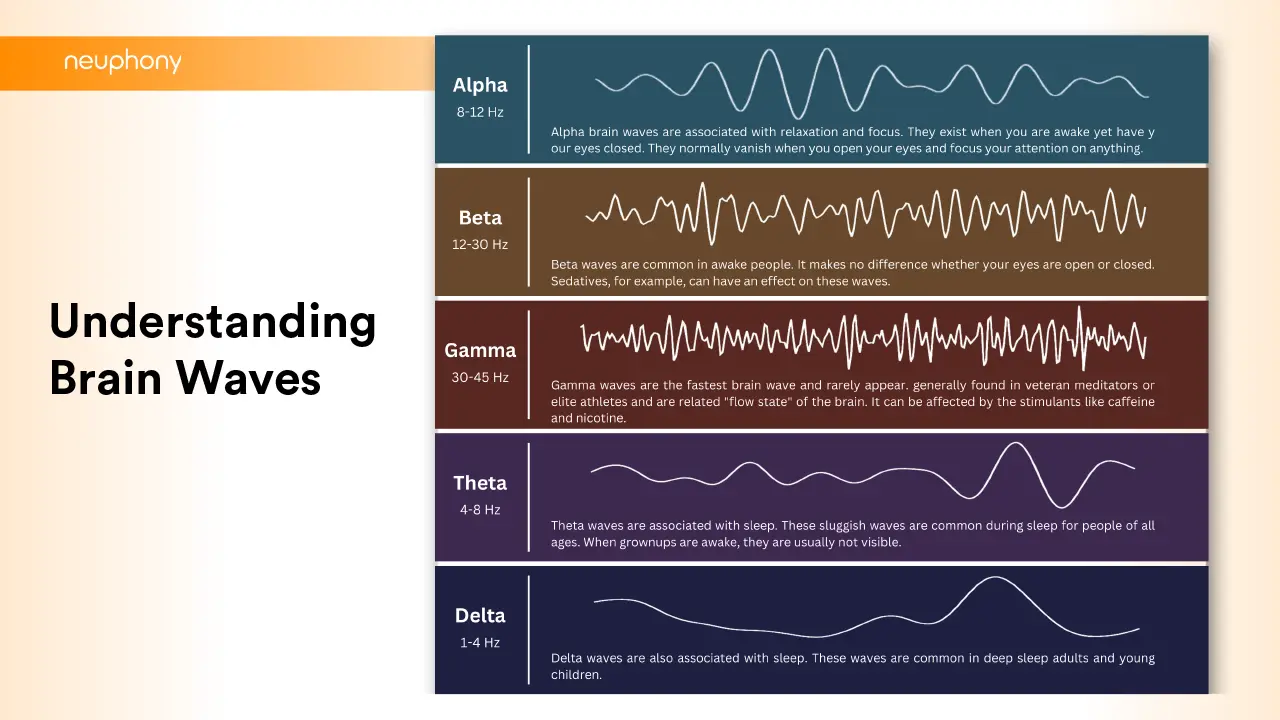
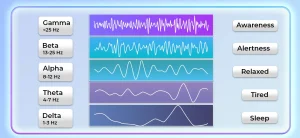
The Different Types of Brain Waves
- Alpha Waves:
Alpha waves, which oscillate at a frequency of 8 to 13 cycles per second (Hz), are most active during states of wakeful relaxation and daydreaming. People often associate them with a calm, relaxed mental state and believe they play a role in enhancing creativity and problem-solving abilities. Activities such as meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can increase alpha wave activity, promoting a sense of inner peace and well-being.
- Beta Waves:
Beta waves, ranging from 14 to 30 Hz, dominate during periods of heightened mental activity and focus. They are most active when you’re awake and alert, helping you stay engaged and productive throughout the day. However, excessive beta wave activity can lead to feelings of stress and anxiety, so it’s important to strike a balance between focus and relaxation in your daily life.
- Gamma Waves:
Gamma waves, with frequencies above 30 Hz, are involved in the integration of sensory information and the coordination of neural networks. Higher-order cognitive functions, such as memory consolidation, learning, and problem-solving, associate with them. Moreover, boosting gamma wave activity through meditation, exercise, and cognitive training enhances cognitive performance and mental clarity.
- Delta Waves:
Delta waves, which have frequencies below 4 Hz, are most prominent during deep sleep and unconscious states. They play a crucial role in promoting restorative sleep and facilitating the body’s natural healing processes. Delta waves during sleep restore energy and repair cells, crucial for physical and mental health.
- Theta Waves:
Theta waves work at frequencies between 4 and 8 Hz, affecting the body with deep relaxation, creativity, and meditation. These mystical waves bridge the subconscious mind, facilitating access to buried memories, intuitive insights, and vivid imagery. Theta waves are prevalent during dream states, hypnosis, and deep meditation, offering a pathway to inner exploration and emotional healing.
The Impact of Brain Waves on Mental Health
Research published by the Department of Physiological Sciences, University of Brasilia, has shown that imbalances in brain wave patterns can contribute to various mental health conditions, including conditions like anxiety, depression, ADHD, and PTSD. Anxiety: excess beta waves; Depression: reduced alpha waves. By understanding these patterns, consequently, neurofeedback or modulation techniques can manage symptoms, improving quality of life.
Harnessing Brain Waves for Personal Growth and Wellness
In recent years, advancements in technology have made it possible to harness the power of brain waves for personal growth and wellness. EEG headsets and apps track brain waves frequency, revealing real-time mental states and patterns. This feedback can be used to optimize daily routines, improve sleep quality, enhance cognitive performance, and manage stress more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, therefore, brain waves profoundly shape our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Additionally, they serve as vital conduits, aiding in understanding the complexities of the human mind. “Understanding brain waves reveals human mind workings, unlocking growth and wellness potentials. Consequently, through meditation, training, and mindfulness, we harness brain waves for happier, healthier lives.