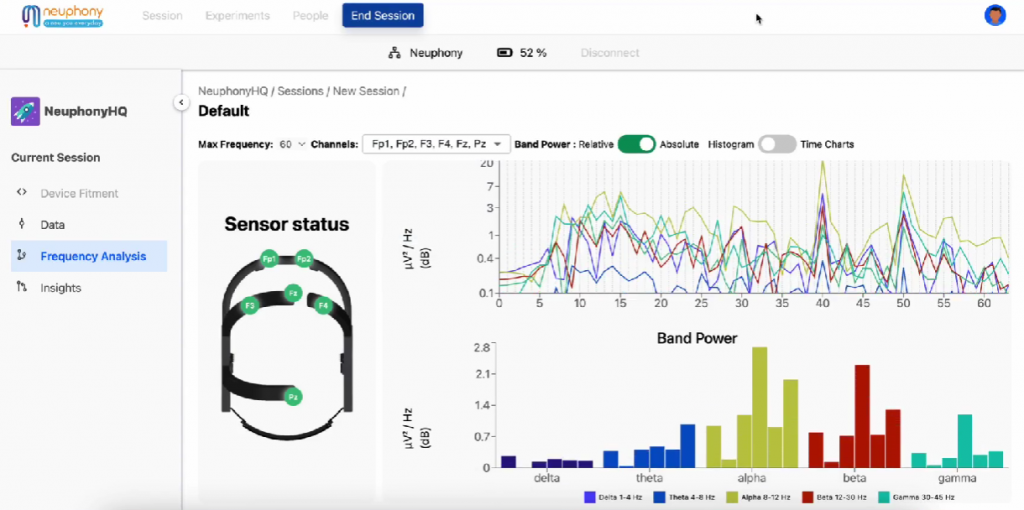
The desktop app of “Neuphony” consists of five distinct parameters:
- Focus
- Relaxation
- Vigilance
- Mental Fatigue
- Mood
- PDR
These parameters serve as measurable indicators of various cognitive states experienced by the user. Focus refers to the ability to concentrate and direct attention towards a specific external task or objective. It is a measure of how effectively one can filter out distractions and maintain concentration. Relaxation, on the other hand, pertains to a state of calmness and reduced stress. This parameter gauges the user’s level of mental relaxation, indicating their ability to unwind and recover from demanding activities.
Vigilance signifies the state of being alert and attentive. It measures the user’s ability to stay vigilant and respond promptly to stimuli or changes in their environment. Lastly, mental fatigue represents the degree of exhaustion or weariness experienced by the user’s cognitive faculties.
It reflects the depletion of mental resources due to prolonged mental exertion or demanding tasks. By monitoring and assessing these parameters, the desktop app can provide valuable insights into the user’s cognitive states and help optimize their productivity, well-being, and overall performance.
Let me give you a better understanding how these parameters are calculated and how they can help you understand your brain better.
Focus:
Beta brain wave activity, which may be quantified via electroencephalography (EEG), has been linked to focus. The brain’s electrical activity is captured by EEG, which classifies it into several frequency bands, including beta waves. When the brain is in a concentrated, awake, and active mental state, beta waves are frequently seen. Their frequency range is about between 13 and 30 Hz. It is possible to determine a person’s degree of attention by examining the magnitude and patterns of beta waves. For example, When someone starts meditating, their mind could start to stray and things might come to mind. This suggests a lack of concentration.
However, when the person continues to meditate and returns their concentration to the selected anchor, the brain’s beta wave activity starts to rise, signalling a greater degree of focus. People can achieve a more continuous and honed attention during meditation with regular practice.
Relaxation:
The alpha and theta brain wave activity can be used to determine how relaxed you are. Theta waves are linked to extreme relaxation and sleepiness, whereas alpha waves are connected to a calm and peaceful frame of mind. The degree of relaxation may be assessed using Neuphony’s EEG technology by measuring the amplitude and frequency of these brain waves. E.g. Consider gradual muscular relaxation as an illustration of a shifting relaxation.
When people are in a normal condition and commencing the progressive muscle relaxation exercise, their alpha and theta wave activity may be rather modest. However, the brain starts to create more alpha and theta waves when they start to consciously relax their muscles and let go of stress. This rise in theta and alpha activity suggests a more profound state of relaxation.
Vigilance:
Beta brain wave activity may also be used to determine vigilance. The amount of alertness may be determined using beta waves, which are linked to an attentive and concentrated state. Changes in alertness may be seen by examining the amplitude and frequency of beta waves using EEG equipment. For example, During the puzzle-solving process, the individual’s vigilance may fluctuate.
For instance, when faced with a challenging aspect of the puzzle, their beta wave activity may intensify, demonstrating heightened vigilance to overcome the obstacle. Conversely, if they become fatigued or lose interest, their beta wave activity may decrease, indicating a decrease in vigilance.
Mental Fatigue:
The activity of the alpha and gamma brain waves can be used to estimate mental tiredness. Gamma waves are linked to cognitive processing and concentration, whereas alpha waves, as previously established, are related to relaxation. The degree of mental weariness may be assessed using EEG technology by measuring the amplitude and frequency of these brain waves.
Let’s use the example of prolonged study or work sessions to show how mental fatigue can change over time. Alpha and gamma wave activity in the brain may initially be balanced when someone starts a study or work session. Gamma wave activity rises during cognitive tasks, indicating active mental processing and attention.
These alterations in brain wave activity can reveal information about the person’s level of mental tiredness. The desktop application can assist users control their cognitive strain and prevent excessive mental weariness by monitoring and analysing the alpha and gamma wave patterns. It can identify indicators of mental fatigue and give feedback.
Mood:
In the context of brain waves, mood refers to a person’s emotional state or attitude. Although individual brain wave patterns are not directly linked to particular emotions, they can be linked to various mood states. Furthermore, depending on the identified mood states, the data can be used to provide tailored suggestions or treatments. For instance, you can attempt relaxation techniques or mindfulness activities to help you calm down and improve your mood if your brain wave patterns show signs of a stressful or anxious mood.
PDR:
In example, when a person is comfortable and resting with their eyes closed, the posterior dominant rhythm is a typical and predominate pattern of brain waves in the posterior area. It is characterised by rhythmic oscillations in the alpha frequency range (8–12 Hz) and is linked to a serene and tranquil state of mind. A person’s brain activity and general cognitive performance can be inferred from the presence and intensity of the posterior dominant rhythm. Deviations or anomalies in the PDR pattern may be symptoms of underlying diseases or dysfunctions of the brain.
In conclusion, brain wave activity measurements of focus, relaxation, vigilance, mental fatigue, mood, and PDR provide important insights into a person’s cognitive states and wellbeing. These factors have real-world uses that are helpful to people in different ways. Overall, incorporating these characteristics into daily life gives people the ability to better understand and utilise their cognitive talents, which boosts productivity, well-being, and overall success in both personal and professional endeavours.

